If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
How to Cut a Quartz Glass Sheet?
Content
What is a Quartz Glass Sheet?
Quartz glass is a special type of industrial technical glass composed of a single component, silicon dioxide (SiO2). Its physical and chemical properties are unique, with the following key features:
- High-temperature resistance: With a softening point of up to 1730°C, quartz glass can operate stably at very high temperatures for extended periods.
- Corrosion resistance: With the exception of hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid, quartz glass is virtually unreactive with any acid, exhibiting excellent chemical stability.
- High light transmittance: It has high transmittance across the entire spectrum from ultraviolet to infrared, particularly in the ultraviolet, which is unmatched by ordinary glass.
- Extremely low thermal expansion coefficient: This means it is insensitive to temperature changes and is not prone to cracking even when subjected to extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Excellent electrical insulation: Even at high temperatures, quartz glass remains an excellent electrical insulator.
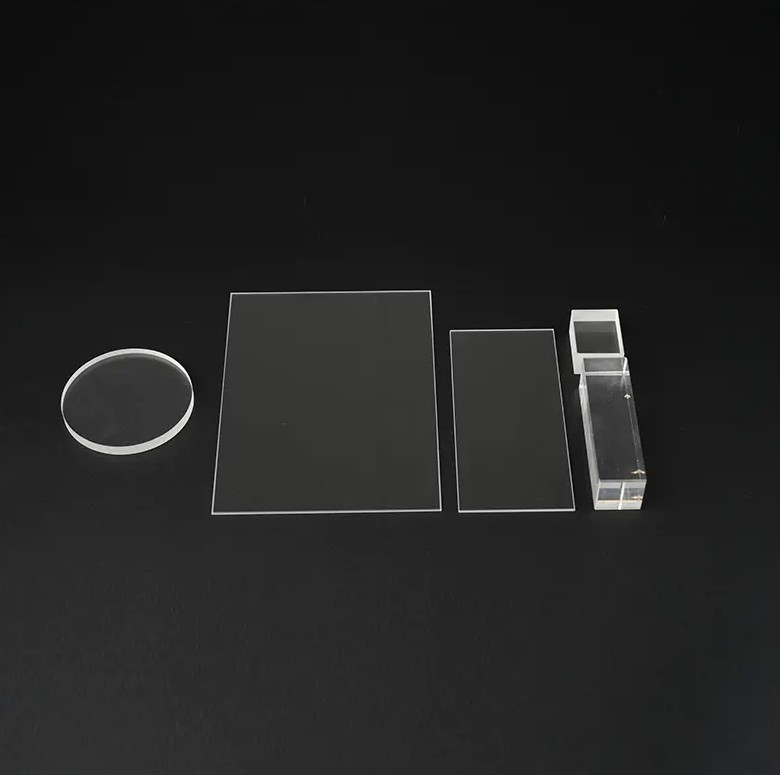
Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, such as high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and high light transmittance, Quartz Glass Sheets are widely used in a variety of high-tech fields, including semiconductors, optics, photovoltaics, and chemicals. However, due to its high hardness and brittleness, cutting quartz glass sheets is a delicate and challenging task.
Common Quartz Glass Sheet Cutting Methods
To successfully cut quartz glass sheets, several specialized methods are commonly employed:
Diamond wire sawing
This is an efficient and high-precision cutting method. Diamond wire saws use a high-speed rotating metal wire (with diamond particles attached to its surface) to grind and cut the material. This method achieves ultra-thin cuts with smooth, minimal cracking, making it particularly suitable for applications requiring the highest precision.
Laser cutting
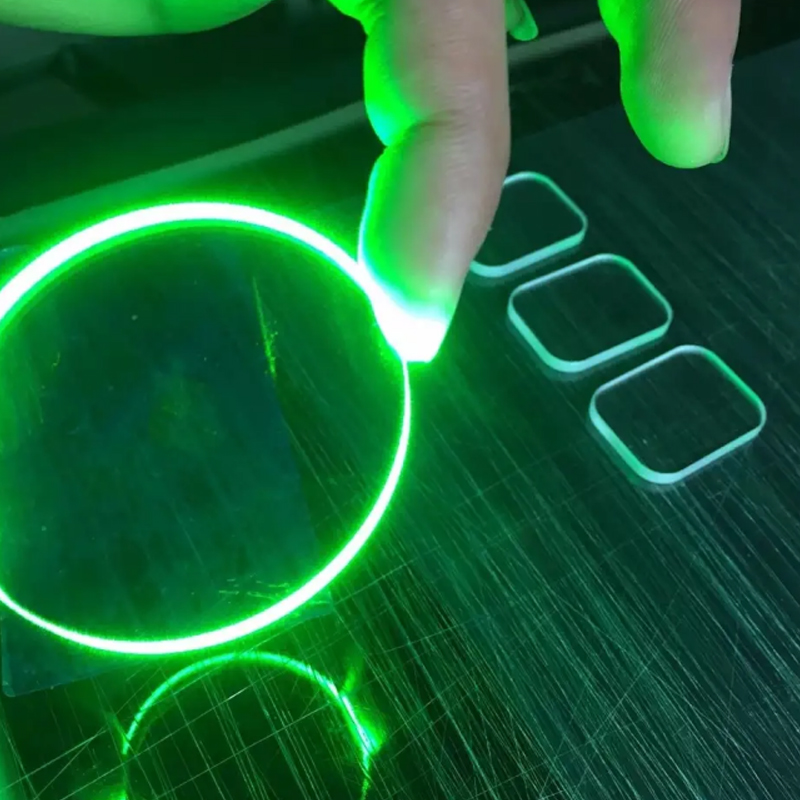
Laser cutting is a non-contact processing technology that uses a high-energy-density laser beam to melt and vaporize the quartz glass sheet, achieving the desired effect. Its advantages include high cutting speed, a high degree of automation, and the ability to cut complex curves and special shapes without the need for additional grinding or polishing. However, it is important to control the laser power and parameters to avoid microcracks or thermal stress on the cut edge.
Waterjet cutting
Waterjet cutting uses a mixture of high-pressure water and abrasives (such as garnet sand) to erode quartz glass sheets. This method generates no heat, thus preventing thermal damage or stress concentration in the material. Advantages include its ability to cut thicker materials and produce a smooth cut surface. However, the cut edges may be slightly abraded, requiring subsequent treatment.
Ultrasonic cutting
Ultrasonic cutting uses a high-frequency vibrating tool to micro-vibrate the surface of the quartz glass. This method achieves precise, heat-free cutting and is particularly suitable for cutting small or thin quartz glass sheets.
Precautions for Cutting Quartz Glass Sheets
- Choosing the Right Equipment: Different cutting methods require specialized equipment, such as diamond wire saws or laser cutters.
- Cooling System: Effective coolant or cooling systems must be used to reduce heat and avoid thermal stress cracking.
- Cutting Parameter Control: Precisely control cutting speed, pressure, and power depending on thickness and size requirements.
- Post-cutting: Polishing or grinding edges after cutting improves surface finish and reduces stress risks.
Cutting quartz glass sheets requires selecting the most appropriate specialized cutting technology based on specific application requirements, taking into account cost, precision, and efficiency.
What is quartz glass?
Quartz glass is a specialized industrial technical glass composed solely of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Its physical and chemical properties are unique, with the following key features:
- High-temperature resistance: With a softening point of up to 1730°C, quartz glass can operate stably at very high temperatures for extended periods.
- Corrosion resistance: Quartz glass exhibits excellent chemical stability, being virtually unreactive with all acids except hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid.
- High light transmittance: It has high transmittance across the entire spectrum from ultraviolet to infrared, particularly in the ultraviolet, which is unmatched by ordinary glass.
- Extremely low thermal expansion coefficient: This means it is insensitive to temperature changes and is not prone to cracking even when subjected to drastic temperature fluctuations.
- Excellent electrical insulation: Quartz glass remains an excellent electrical insulator even at high temperatures.
Due to these excellent properties, quartz glass sheets are widely used in a variety of high-tech and industrial fields, including semiconductors, optics, photovoltaics, chemicals, laboratory equipment, and electric light sources.

 +86-0515-86223369
+86-0515-86223369  en
en English
English 日本語
日本語 Español
Español