If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What are quartz glass tubes used for?
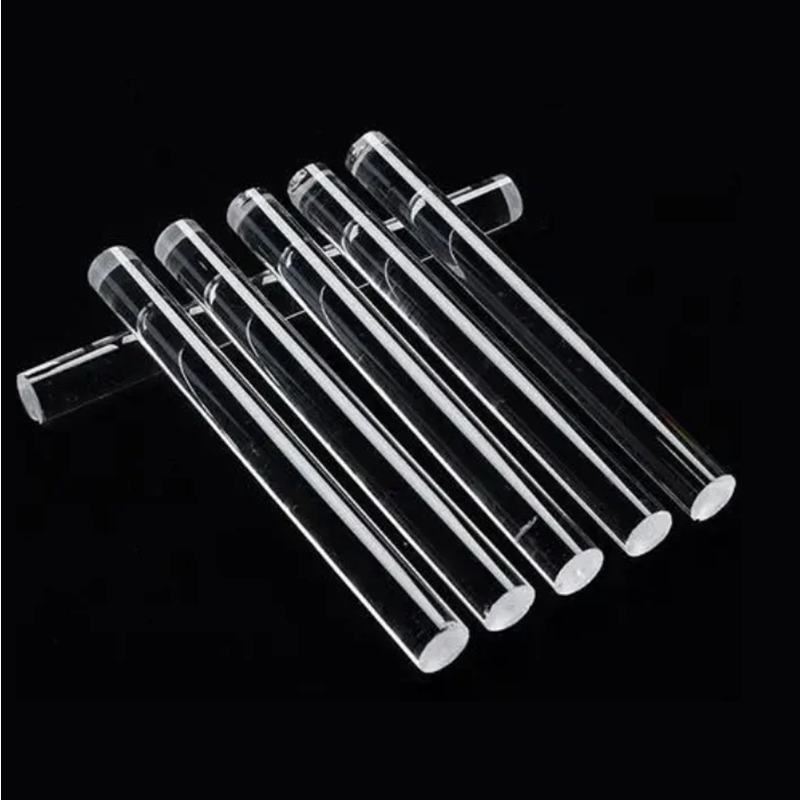
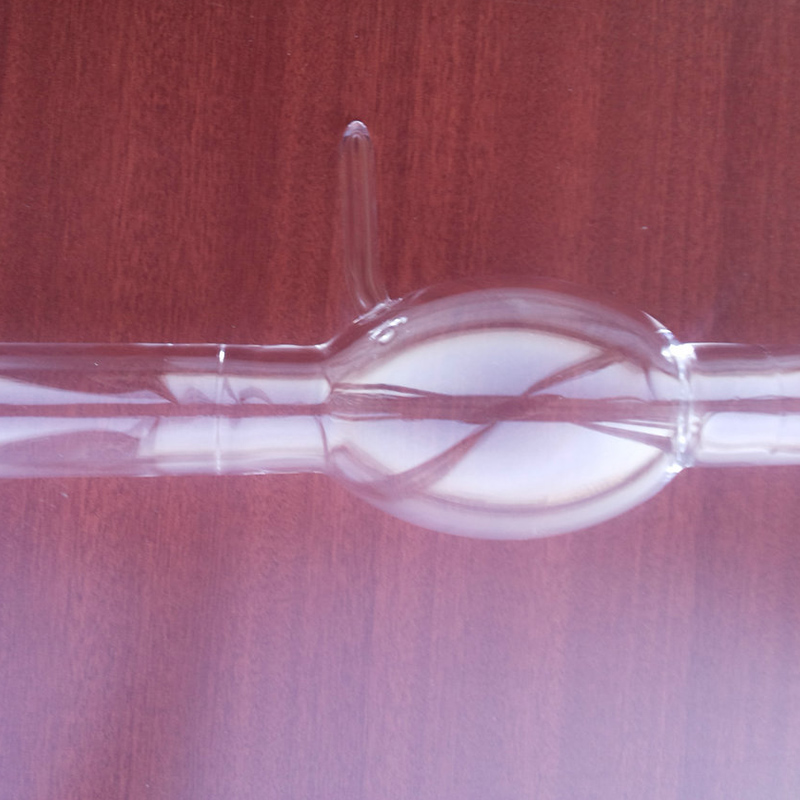
Quartz glass tubes, a special industrial technical glass composed of a single component of silicon dioxide, play an irreplaceable role in modern high-tech fields due to their exceptional physical and chemical properties. They are not only common laboratory equipment but also core components in numerous high-tech industries. So, what are the amazing uses of this seemingly ordinary quartz glass tube?
Content
1. High-Temperature Heat Treatment and Lighting: A Model of High-Temperature Resistance
The most outstanding characteristic of quartz glass tubes is their extremely high heat resistance. With a softening point approaching 1700°C, they can withstand temperatures up to 1100°C for extended periods.
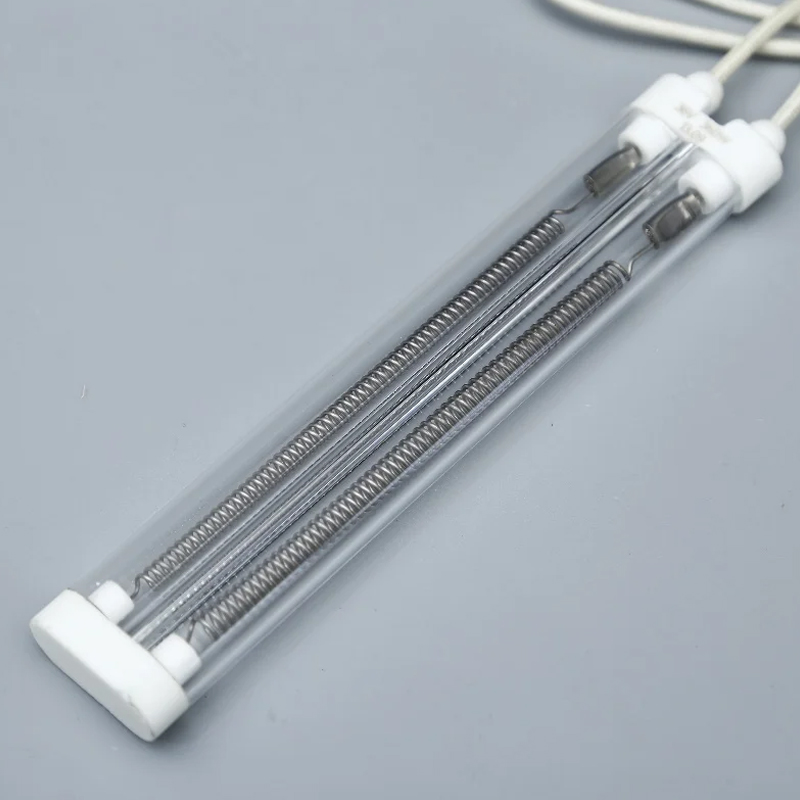
High-Temperature Furnace Tubes and Heat Treatment Equipment: In industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, and chemicals, quartz tubes are often used as furnace tubes in high-temperature diffusion furnaces, annealing furnaces, and CVD (chemical vapor deposition) equipment, providing a pure, stable, high-temperature environment.
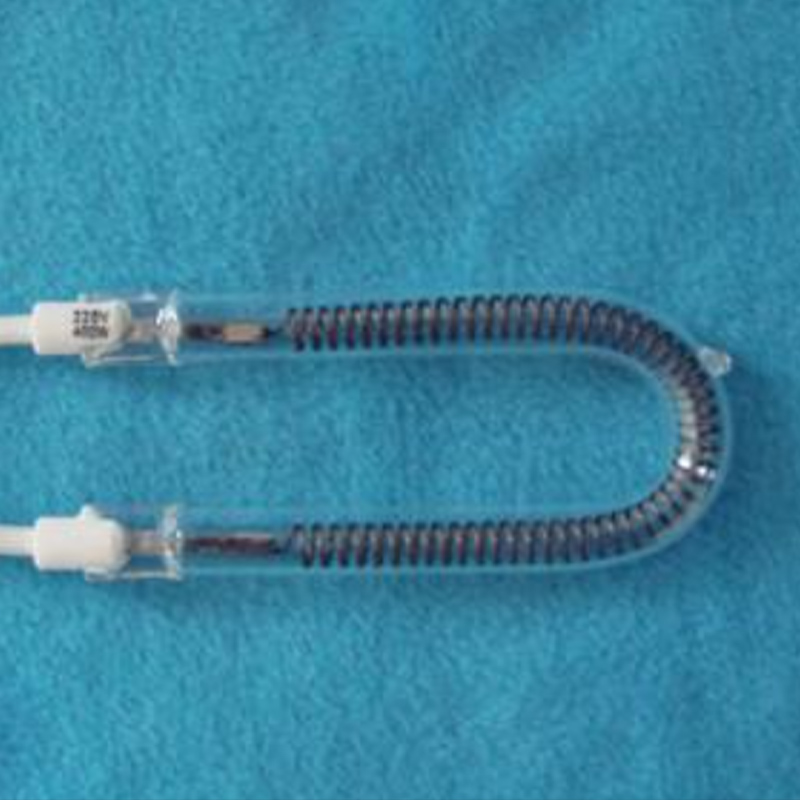
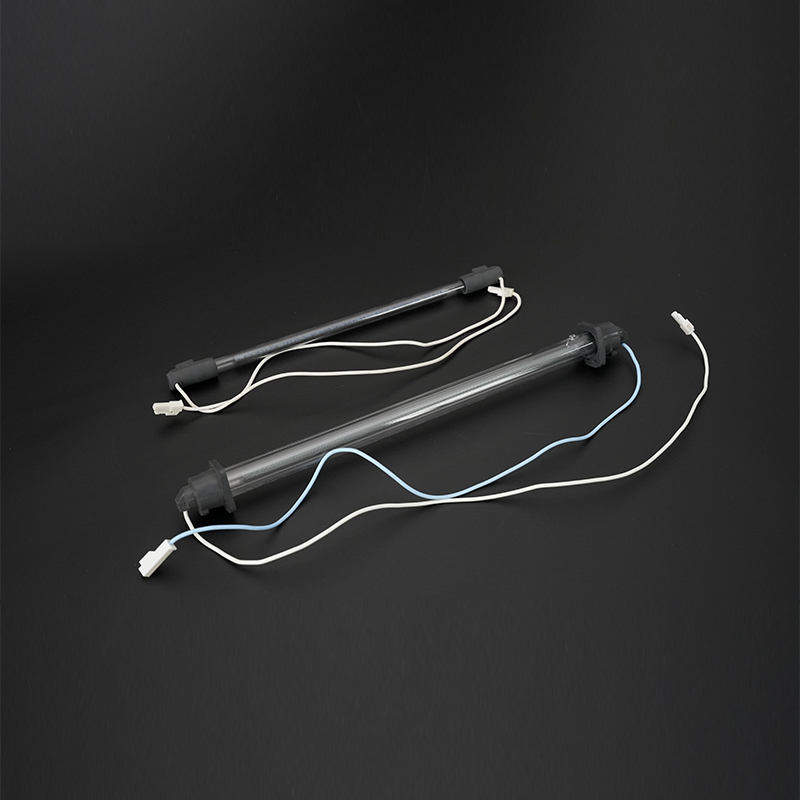
Light Sources and Lighting: The housings and arc tubes of high-performance light sources such as high-pressure mercury lamps, halogen lamps, and xenon lamps are made of quartz glass tubes. This is because quartz tubes have extremely high light transmittance, especially in the ultraviolet (UV) band, making them ideal for manufacturing specialty light sources such as germicidal lamps and UV curing lamps.
2. Semiconductor Manufacturing: An Indispensable "Container"
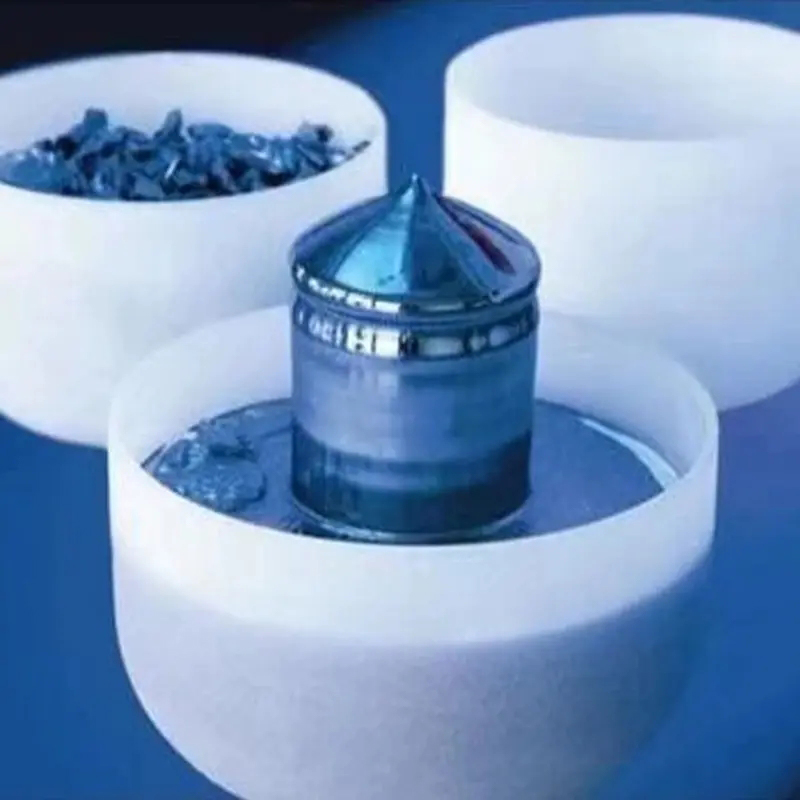
The semiconductor industry demands extremely high material purity. Quartz glass tubes, due to their ultra-high purity (typically exceeding 99.99% silicon dioxide content) and excellent chemical inertness, have become key consumables in this field.
Wafer Processing Equipment: In the wafer manufacturing process for integrated circuits (ICs) and solar cells (photovoltaic), quartz tubes are used to hold wafers or serve as reaction chambers in key steps such as oxidation, diffusion, and etching.
Quartz Boats and Quartz Devices: Derivative quartz products such as quartz boats and crucibles are used to hold wafers, ensuring that impurities are not introduced during high-temperature processes.
3. Optics and Communications Technology: Excellent Light Transmission
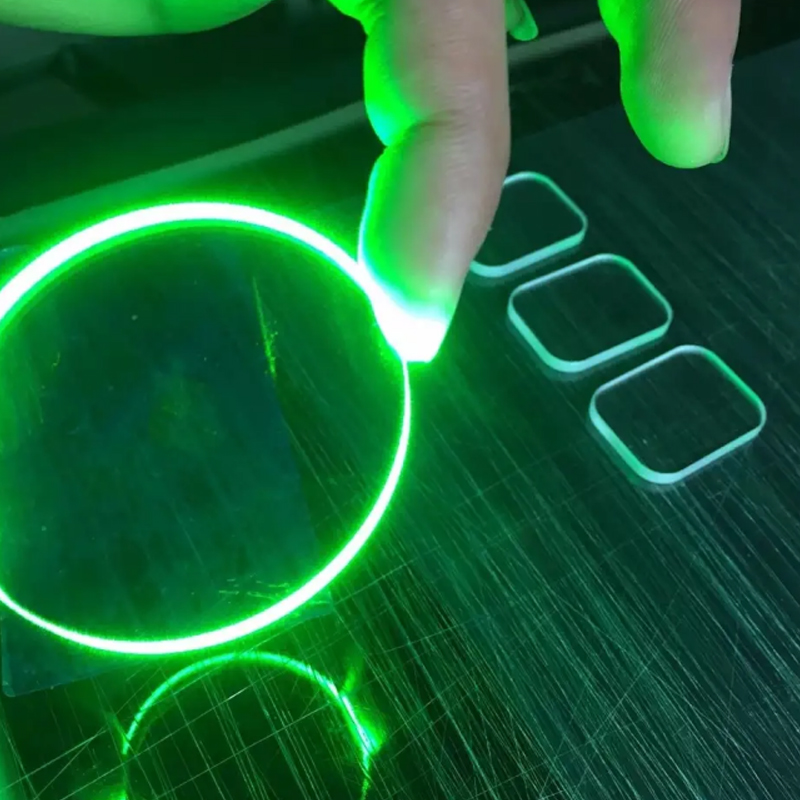
Quartz glass tubing exhibits extremely high light transmittance across a wide spectral range, from ultraviolet to infrared, making it a high-quality optical material.
Fiber Optic Preform: High-purity synthetic quartz tubing is a key raw material for drawing optical fiber preforms, ensuring high-speed and low-loss information transmission.
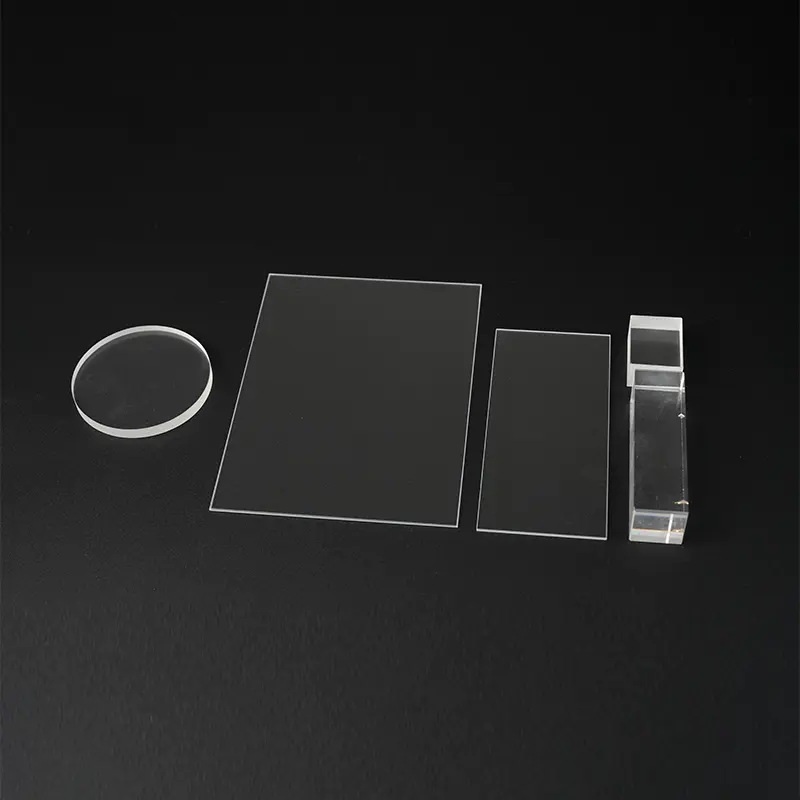
Optical Instrument Windows: Quartz tubing and quartz sheets are often used as optical windows, prisms, or lenses in UV spectrophotometers, laser equipment, and aerospace optical instruments because of its high UV transmittance, which is unmatched by ordinary glass.
4. Chemical and Laboratory Applications: Corrosion Resistance
Quartz tubing is not only resistant to high temperatures but also extremely chemically resistant. It exhibits excellent stability against acids other than hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid.
Chemical Reaction Vessels: Quartz glass tubing is often used as reactors or containers such as quartz beakers in experimental and industrial chemical processes such as high-purity reagent preparation, catalytic reactions, and distillation, preventing metal ion contamination.
Quartz glass tubes, with their unique "three highs and one low" properties—high temperature resistance, high light transmittance, high chemical purity, and low thermal expansion coefficient—occupy a core position in industries requiring high temperature, high purity, and high precision. Whether driving semiconductors and optical communications in the information age or ensuring high-quality light sources in the lighting industry, quartz glass tubes serve as a key quartz component, providing a solid foundation for technological development.
- Tel:
+86-0515-86223369
+86-15754187666 - WeChat:
+86-13485219766 - WhatsApp:
+86-13485219766 - E-mail:
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:
NO.33,yuejinRoad,Science And Technology Pioneer Park,hengji Town,jiangsu county,yancheng city,jiangsu province,china 224763, China
Copyright © Yancheng Mingyang Quartz Products Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Wholesale Quartz Products Manufacturer Quartz Glass Factory
 +86-0515-86223369
+86-0515-86223369  en
en English
English 日本語
日本語 Español
Español