If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What are the differences between quartz crucibles and silica crucibles?
In industries involving high-temperature melting and precision material preparation, the terms "Quartz crucibles" and "silica crucibles" are frequently used. To accurately understand their differences, the key lies in the purity of the raw materials, the precision of the processing technology, and the final application standards.
Content
Core Difference: Purity Determines Application Grade
The most fundamental difference between Quartz crucibles and silica crucibles lies in the purity and impurity control of silica.
Quartz Crucible
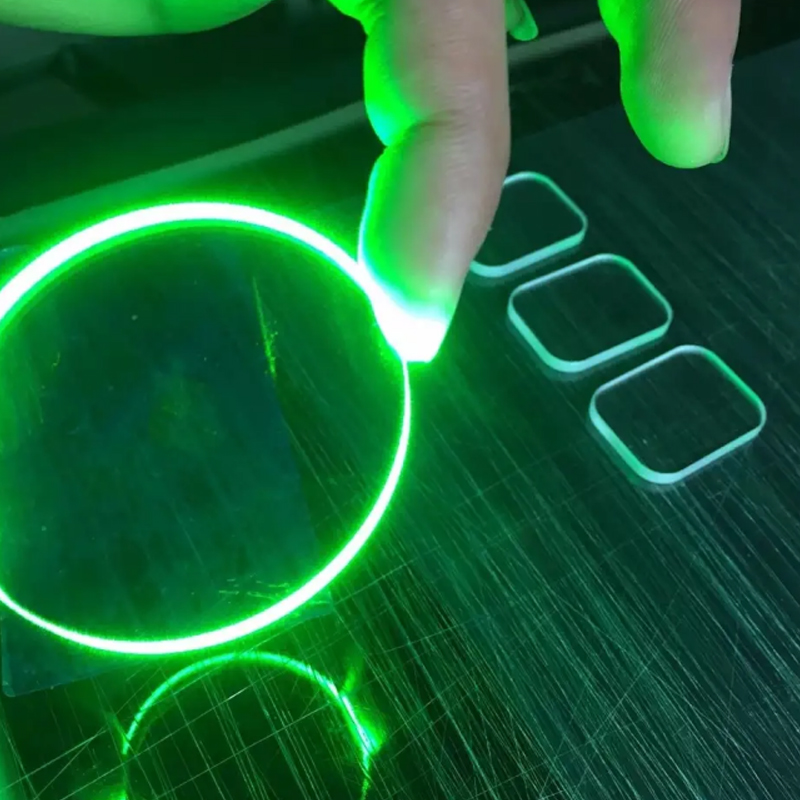
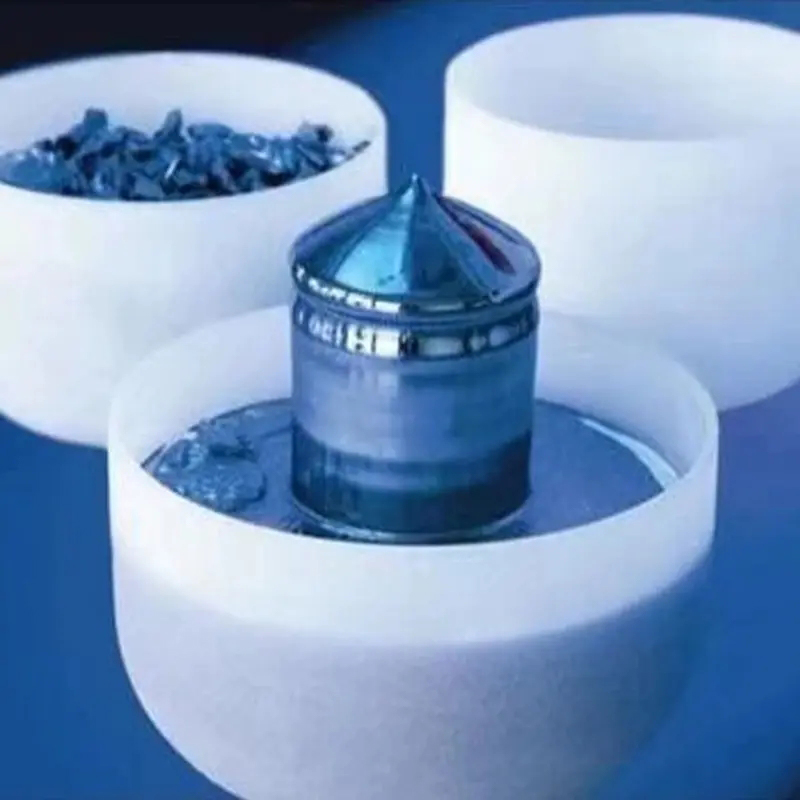
High Purity Core: Quartz crucibles have extremely high manufacturing requirements. They are mainly made from high-purity quartz sand (high-purity quartz) through a series of complex and rigorous purification processes including melting, drawing, and sintering.
Key Indicators: Silica purity is typically required to reach 99.99% or higher, with extremely low limits on the content of metallic impurities.
Structure and Performance: Possesses excellent chemical inertness and thermal stability. Its structural design (such as transparent and opaque layers) is intended to prevent contamination of the molten material and provide a uniform heating environment at extremely high temperatures (such as the pulling temperature of monocrystalline silicon).
Main Applications: Specifically designed for fields with extremely high purity requirements, such as the growth of monocrystalline silicon in the photovoltaic industry and the refining of semiconductor materials.
Silica Crucible
Raw Material Definition: "Silica" is a general term for quartz minerals. Therefore, "silica crucible" can broadly refer to any container made from natural quartz minerals.
Purity Limitations: If specifically referring to non-high-purity products, the raw materials for these crucibles are less purified, with silica purity far lower than that of quartz crucibles, containing more structural impurities.
Performance and Applications: Due to the high impurity content, these impurities are easily released and enter the molten system at high temperatures, affecting the electrical or mechanical properties of the final material. Therefore, they are not suitable for photovoltaic and semiconductor crystal growth, which require stringent purity standards.
In the context of modern high-tech manufacturing
Quartz crucibles represent high-purity, high-precision silicon dioxide products; while silica crucibles often imply lower purity, limiting their application range.
Quartz crucibles are key strategic consumables in the photovoltaic and semiconductor industry chain, and their technological level directly affects the efficiency and cost of the entire downstream industry:
Size and Efficiency: With the expansion of GW-level silicon rod production capacity, there is an urgent need for larger and longer-lasting quartz crucibles. A high-quality crucible can effectively reduce amorphous silicon deposition and scrap rates during the production process.
Impurity Control: The purification process is a core barrier. How to efficiently and cost-effectively remove impurities such as Al and Fe is a reflection of the technological leadership of leading crucible suppliers.
The core difference between quartz crucibles and silica crucibles lies in their purity level and manufacturing precision. Quartz crucibles are precision products that undergo rigorous purification processes, possessing extremely high silica purity and excellent heat resistance, and are key strategic consumables for the photovoltaic and semiconductor industries in manufacturing monocrystalline silicon. Conversely, "silicon crucible" usually refers to a container made of low-purity silica, whose impurity content makes it unable to meet the almost demanding requirements of modern high-tech industries for material purity.
- Tel:
+86-0515-86223369
+86-15754187666 - WeChat:
+86-13485219766 - WhatsApp:
+86-13485219766 - E-mail:
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:
NO.33,yuejinRoad,Science And Technology Pioneer Park,hengji Town,jiangsu county,yancheng city,jiangsu province,china 224763, China
Copyright © Yancheng Mingyang Quartz Products Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Wholesale Quartz Products Manufacturer Quartz Glass Factory
 +86-0515-86223369
+86-0515-86223369  en
en English
English 日本語
日本語 Español
Español