If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Are the Differences Between Quartz Crucibles and Silicate Crucibles?
In industries such as high-temperature materials, semiconductors, and new materials, the choice of crucible directly affects product quality and production efficiency. So, what are the differences between quartz crucibles and silicate crucibles? Quartz crucibles use high-purity silicon dioxide as the main raw material, offering high temperature resistance, high purity, and strong thermal stability. Silicate crucibles, on the other hand, are based on various silicate minerals, resulting in lower cost, but their temperature resistance and chemical stability are relatively limited.
Content
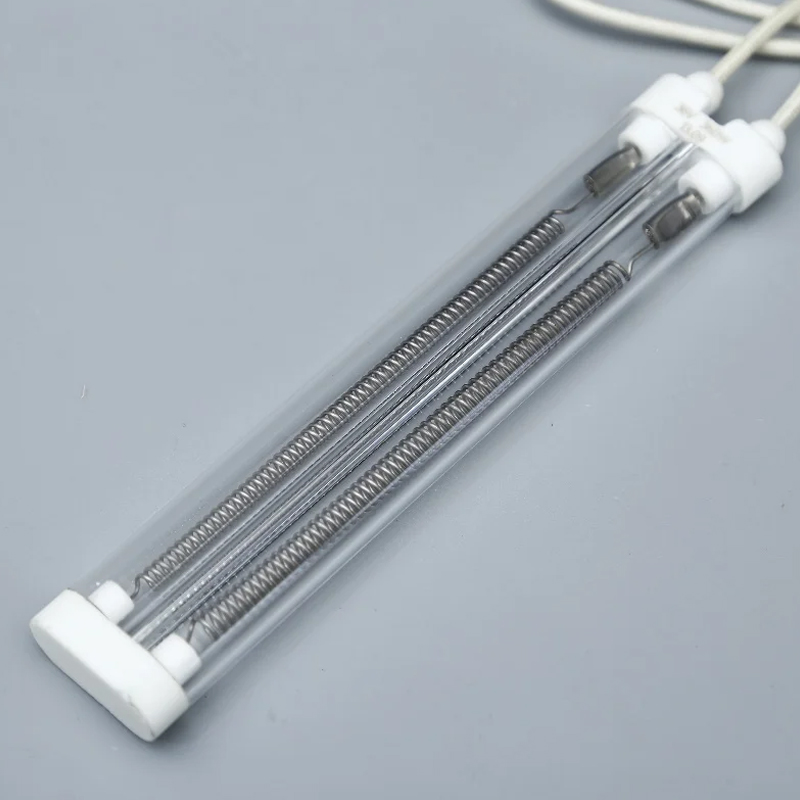
Materials and Performance Characteristics of Quartz Crucibles
Quartz crucibles are mainly made from melted high-purity quartz sand, with a silicon dioxide content typically exceeding 99.9%. This high purity determines its irreplaceable role in high-end applications.
In terms of performance, quartz crucibles have the following advantages:
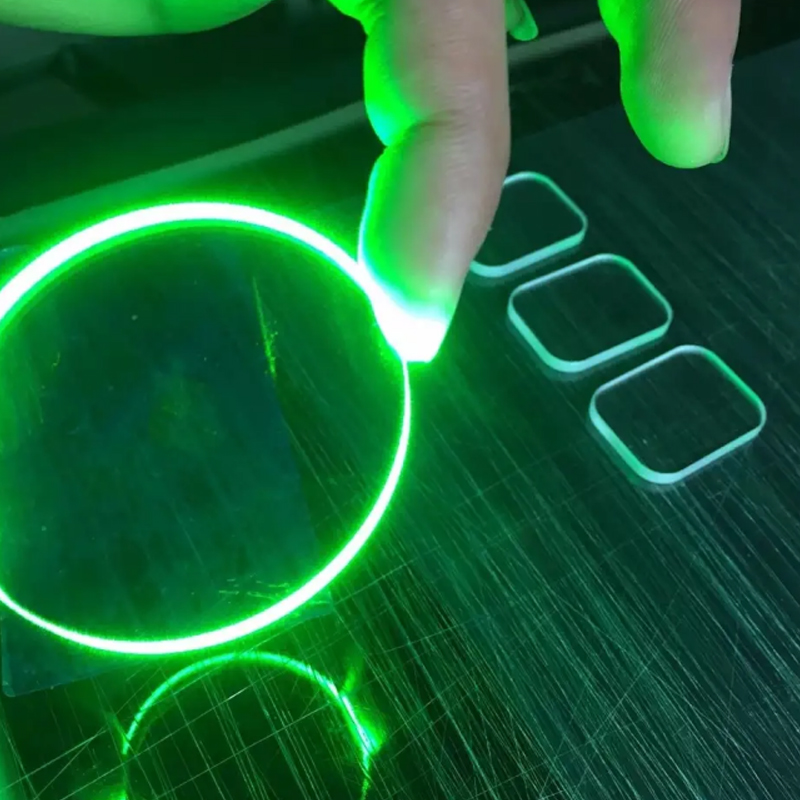
Outstanding high-temperature resistance: Can be used continuously at temperatures above 1600℃, suitable for melting single-crystal silicon and semiconductor materials.
Good thermal stability: Low coefficient of thermal expansion, less prone to cracking due to rapid heating and cooling.
Strong chemical stability: Excellent resistance to most acids and molten metals. Because of these characteristics, quartz crucibles are widely used in photovoltaics, semiconductors, and precision materials processing.

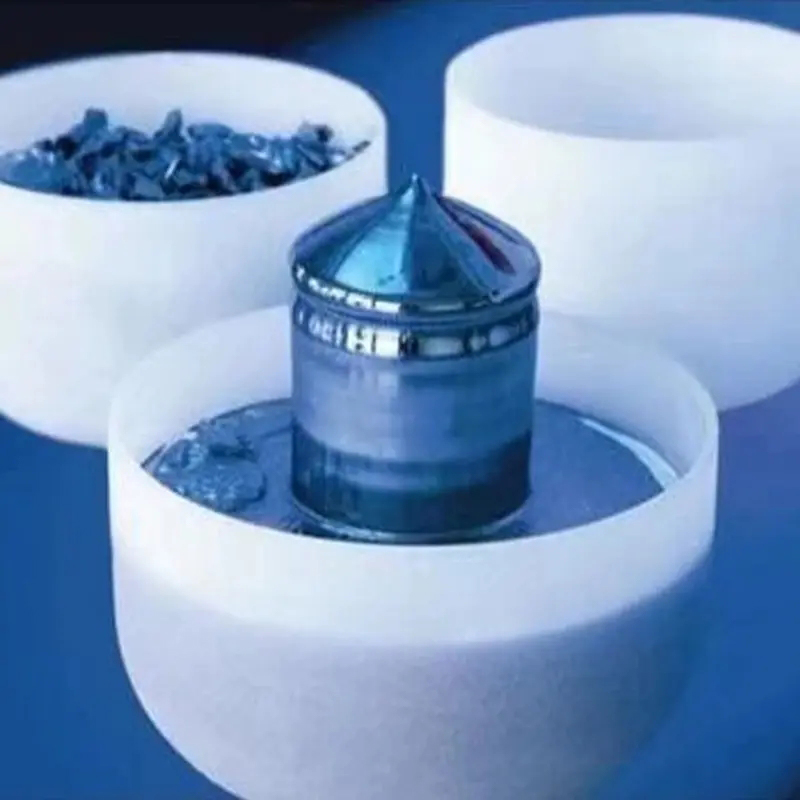
Silicate Crucibles: Structure and Applications
Silicate crucibles are typically made from a variety of silicate raw materials. The raw materials are widely available, and the production process is relatively mature, resulting in lower costs. Silicate crucibles still have a certain market in some metallurgical, laboratory, or general industrial heating processes where high purity requirements are not critical.
However, compared to quartz crucibles, silicate crucibles differ in the following aspects:
Lower upper temperature resistance: Prone to structural changes under long-term high-temperature environments.
Generally lower chemical stability: Easily introducing impurities in highly corrosive or high-purity environments.
Relatively shorter service life: More suitable for low- to mid-range applications.
Key Differences Between Quartz and Silicate Crucibles
The main differences between quartz and silicate crucibles lie in the purity of raw materials, high-temperature resistance, application areas, and operating costs. Quartz crucibles are more geared towards high-end manufacturing and precision industries, while silicate crucibles meet the needs of basic industries and routine experiments.
If the production process demands high material purity, stability, and product consistency, quartz crucibles are more suitable; however, if cost control is a primary concern and the operating conditions are relatively mild, silicate crucibles are equally adequate.
With the rapid development of the photovoltaic, new materials, and semiconductor industries, the importance of quartz crucibles is constantly increasing. Understanding the differences between quartz and silicate crucibles helps companies make more informed material choices in actual production, thereby improving efficiency, reducing risks, and achieving more stable product quality.
- Tel:
+86-0515-86223369
+86-15754187666 - WeChat:
+86-13485219766 - WhatsApp:
+86-13485219766 - E-mail:
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:
NO.33,yuejinRoad,Science And Technology Pioneer Park,hengji Town,jiangsu county,yancheng city,jiangsu province,china 224763, China
Copyright © Yancheng Mingyang Quartz Products Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Wholesale Quartz Products Manufacturer Quartz Glass Factory
 +86-0515-86223369
+86-0515-86223369  en
en English
English 日本語
日本語 Español
Español