If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
How are quartz crucibles manufactured?
Quartz crucibles are essential consumables in the semiconductor and photovoltaic industries, and their manufacturing process directly impacts the quality and cost of silicon crystal growth. Raw material purity and process control are particularly critical in the production of quartz crucibles for single-crystal silicon. So, how are these key components actually made? The following describes two main manufacturing methods to provide a more intuitive understanding of the production process for opaque quartz crucibles for photovoltaics.
Content
Main Production Processes of Quartz Crucibles
Currently, there are two commonly used manufacturing methods: slurry molding and injection solidification (injection molding). While both serve the same purpose—producing high-purity quartz crucibles—they differ in their specific process flows and finished product characteristics.
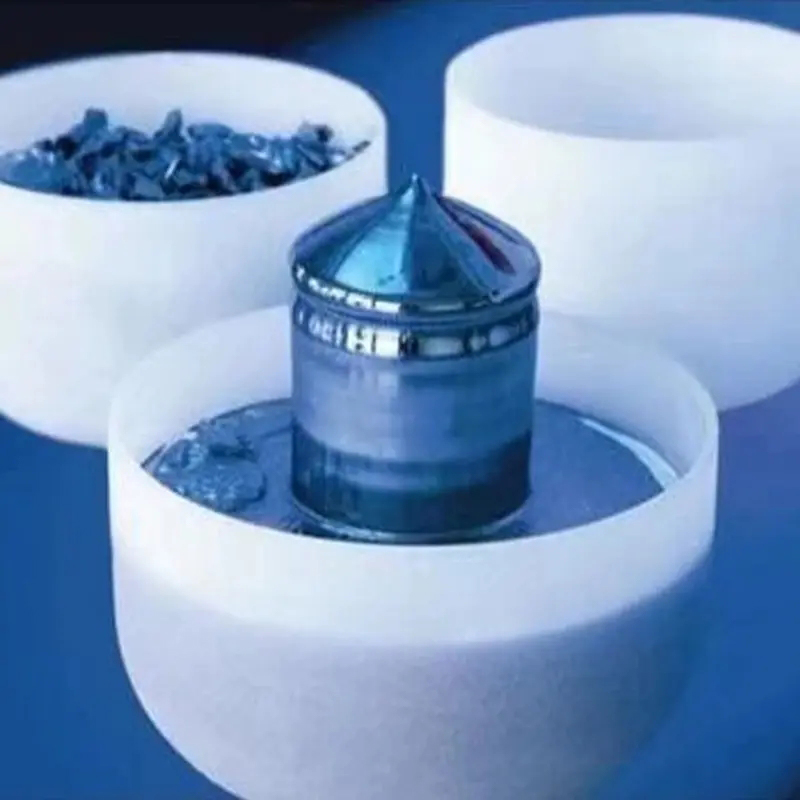
1. Slurry Molding
This is a traditional method for producing single-crystal silicon quartz crucibles for solar cells, and the process is relatively mature.
Raw Material Preparation
Select high-purity quartz sand, grind it into a fine powder, mix it with a binder and other auxiliary materials, and prepare a slurry with a certain degree of fluidity.
Molding
The slurry is poured into a rotating mold and evenly distributed along the mold wall using centrifugal force to form the crucible body. This process requires precise control of the slurry uniformity and mold rotation speed to ensure consistent wall thickness.
Drying and Demolding
The formed body is pre-dried in the mold and carefully demolded once the required strength is achieved.
Sintering
The body is sintered in a high-temperature furnace, allowing the quartz particles to bond at high temperatures, forming a dense structure. The sintering temperature and time directly affect the performance of the finished product.
2. Injection Solidification Method
This is a newer process that has developed rapidly in recent years and is particularly suitable for producing large-scale photovoltaic quartz crucibles.
Slurry Preparation
Similar to the slurry method, it places greater emphasis on the slurry's fluidity and solidification properties. Quartz powder is mixed with a special gelling agent to form an injectable slurry.
Injection Molding
The slurry is injected into a preheated mold using an injection machine. Under specific conditions, the slurry rapidly gels and forms the crucible shape.
Drying and Sintering
After forming, the crucible undergoes thorough drying and high-temperature sintering. Due to the uniform formation, the crucible structure after sintering is denser and more uniform.
Process Comparison
| Features | Slurry production process | Injection solidification process |
| Advantages | Low cost and relatively mature technology. | Produces uniform molding, high product density, and is capable of producing large quartz crucibles. |
| Disadvantages | Crucible wall thickness uniformity is poor, and bubbles may be present. | This process is costly and places higher demands on equipment and slurry formulation. |
| Applications | Production of traditional small single crystal silicon quartz crucibles. | It is used for the production of modern large-scale photovoltaic and specialty quartz crucibles. |
Regardless of the method used, the production of high-quality quartz crucibles requires high raw material purity and meticulous process control. Quartz crucibles are irreplaceable in the semiconductor and photovoltaic fields, ensuring the smooth production of single crystal silicon and its ultimate application in other industrial chains, such as solar energy.
- Tel:
+86-0515-86223369
+86-15754187666 - WeChat:
+86-13485219766 - WhatsApp:
+86-13485219766 - E-mail:
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:
NO.33,yuejinRoad,Science And Technology Pioneer Park,hengji Town,jiangsu county,yancheng city,jiangsu province,china 224763, China
Copyright © Yancheng Mingyang Quartz Products Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Wholesale Quartz Products Manufacturer Quartz Glass Factory
 +86-0515-86223369
+86-0515-86223369  en
en English
English 日本語
日本語 Español
Español